Cold forming
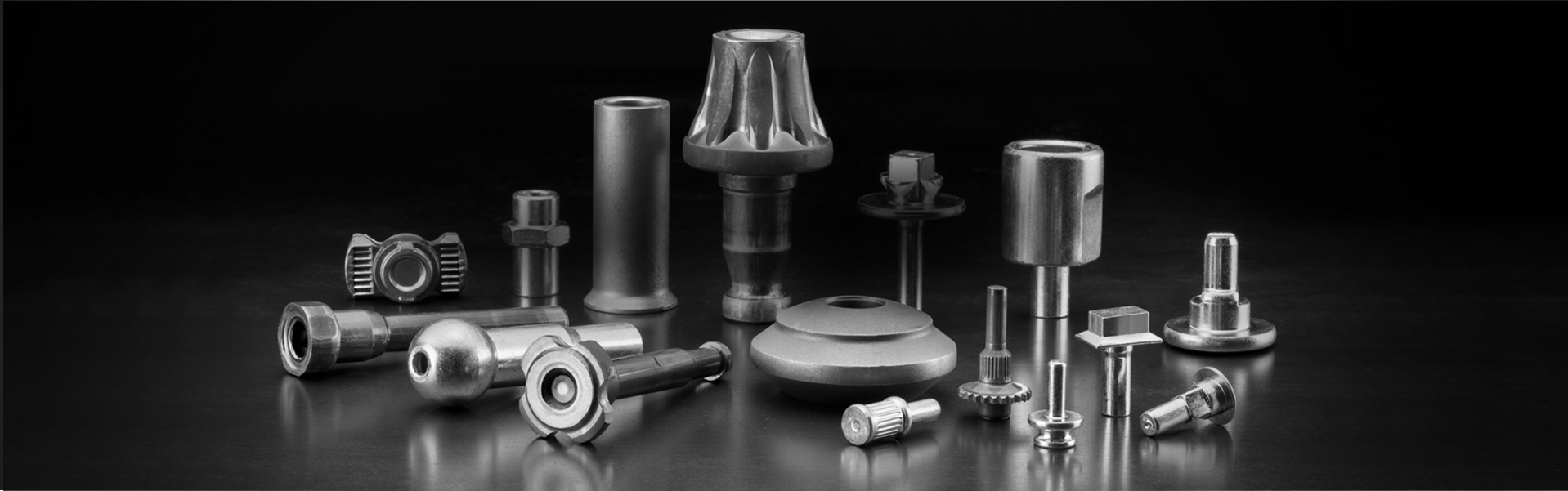
Cold forming is a technology with a great tradition, which continuously reinvents itself and surpasses new limits. TEMSA has more than 30 years’ experience in the design and manufacturing for cold forming projects using multi-station machine. From ball pins, screws, specialized nuts and bolts, gears, special mounting elements, tube rolling, aluminium extrusion, ammunition… an extremely wide range of products.
TEMSA is involved in the majority of the cold forming processes in the market.
From the manufacturing of large orders to single units, TEMSA has the technology needed to help each client with whatever they need.
TEMSA has extensive experience in parts with large section changes or significant requests during the manufacturing process. Especially with parts which require significant extrusion or utilization of modular tools. TEMSA is involved as well in helping costumers where the lack of know how in certain technologies, like the open dies process, represents a barrier to entry to new markets for parts manufacturers. Where there’s a problem needing to be solved is where TEMSA will be.
Cold forming
Cold forming is a process of metal deformation in which the wire is cut to a specific length and deformed at room temperature through its insertion in steel or carbide dies prepared in 2 or more consecutive stations.
This process is carried out by applying very high pressure which deforms the material beyond its elastic limit but without reaching its breaking point. In this way we are able to obtain highly complex parts without producing scrap and at a very high speed, allowing for mass production of identical parts at a significantly reduced price.
There’s a series of basic operations in which all of the processes of cold forming are based on. The principle ones are shearing, reduction, stressing, extruding, piercing, trimming, and burnishing. There’s a tool for each kind of operation, with a geometry, material, and coating specifically adapted to what needs to be obtained.
TECHNOLOGY
Technology has advanced a lot recently and what was once impossible is now normal. A limit is surpassed on a daily basis. Many factors have contributed to this and when combined makes the industry reinvent itself constantly:
Improvements in the materials: carbide is constantly evolving and the sintering equipment for these raw materials keeps bringing specific grades for each type of process. Where before Widia was required, now the exact composition is described, the size of the grain and the necessary properties. This has made it possible to improve the performance of the tool enormously. On the other hand steel is increasingly more specific, with a wide variety of classifications, from high speed steel, powder metallurgical, with supplementary treatments etc, which can even compete with carbide in terms of benefits.
Improvements in machinery used: tool manufacturers use machinery which is increasingly more precise and with better surface treatment. CNC machines with superfinishing, avoiding micro fissures and leaving an Ra which only a few years ago was impossible even imagine. Additionally, presses for cold forming are increasingly faster and better controlled.
Constructive solutions: simulation is a great ally in cold forming, but it’s the imagination and knowledge of the technicians who propose solutions to cut costs and improve performance or even make it possible to manufacture forming parts which previously seemed as if they could only be turned.
In this way the interchangeability of nibs, the application of coating in specific areas, the design improvements and the never ending tests allow us to arrive where once wasn’t possible.
FINISHING
The tolerances must be in accordance with the product being made, with the ability to reach up to 0,005mm. The material used could be carbide or steel, with the ability to use all types of carbide and steel grades- special, high speed, powder metallurgical, etc.- in order to take advantage of the characteristics most adapted to the process in which they’ll be used and so they function better.
Together with the material and the shape, it’s of vital importance that the surface finishes – in the range of Ra0.5- which greatly influences the lifespan of the tool.
COATINGS
In PM coatings are used to improve the properties of some types of tools. Each coating -TiN, TiAlN, AlCrN, amongst others- provides specific supplementary properties to the tool whether it be a punch or a die. TEMSA works with the best companies in the market of coating application in order to offer its clients the best options to increase the performance of their tools.
| Main chemical composition | Way of application | Thicknes | Colour | Field of application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AlCrN | PVD | 2-6mm | Metallic grey | High resistance to oxidation. For pins in piercing and extrusion processes in Cold Forming and Fine Blanking. |
| TiN | PVD | 2-4mm | Golden | The most usual coating for every application: pressing, piercing, reduction and upsetting. |
| TiCN | PVD | 2-4mm | Light silver | A superior coating than TiN. It is used when a higher wear resistance is needed. Decrease of friction when two parts slide against each other. |
| CrTiN | PVD | 6-12mm | Light silver | Suitable for certain applications with stainless steel. |
| TiAlN | PVD | 3-12mm | Grey-violet | It is used when high pressure is created, along with high temperature and chipping can be a problem. |
| DLC | PVD | 1-3mm | Black | Diamong-like-coating. Suitable for applications working with aluminium –either upsetting or extrusion – it prevents the wear out due to the aluminium getting stuck to the surface of the tool. |
| CrN | PVD | 2-4mm | Light silver | In order to reduce the friction coefficient between two surfaces. Higher ductility and thickness than other coatings. It helps to increase the fatigue point and the resistance to breaks, as well as the corrosion and oxidation resistance. |
| WC/C | PVD | 2-5mm | Black | It help to reduce the adherence of materials. There exists the possibility of adding it to other coatings, like AlCrN, as a second duplex coating, in order to improve their performance. |
| TiC or Tin/TiC | CVD | 7-9mm | Metallic grey or golden | Chemical Vapour deposition. PVD means Physical Vapour Deposition). Extreme resistance to wear out and impact. It helps to reduce the friction temperatura. It modifies the estructure of the Surface. |

POWDER METALLURGY
TEMSA is one of the leading players in the pressing and sintering of metal powders.
CARBIDE
TEMSA has developed and manufactured tools specifically for wear and cutting applications in different grades of tungsten carbide.